Let's see the production of cemented carbide and fine ceramics as a concrete example of applying HIP technology. Cemented carbide and fine ceramics are inferior to metals such as steel and aluminum in toughness and very vulnerable to defects such as course particle and pore. It is necessary to remove such internal defects in order to make full use of the natural characteristics of these materials, and HIP is the most effective means to eliminate those defects.
Cemented carbide
Since a liquid phase of metal such as cobalt is utilized as a binder phase in the sintering of cemented carbide, it is possible to compact a normal sintered body nearly up to the theoretical density. However there remain fine pores in the sintered body and they act fatally to the cemented carbide to break under a pressure that can be withstood in normal condition. It is the purpose of HIP treatment to eliminate completely a few pores existing in the sintered body.
Table 1 shows the change in mechanical properties by HIP and Fig.2 shows the Weibull plot of bending strength before and after HIP.
<Table 1> Effect of HIP treatment on mechanical properties of cemented carbide (G2)
| |
Before HIP |
After HIP |
| Relative density [%] |
nealy 100 |
nealy 100 |
| Hardness [HRA] |
91.0 |
91.0 |
| Bending strength [Mpa] |
2450 |
2940 |
Fracture toughness
[Mpa·m1/2] |
10 |
10.5 |
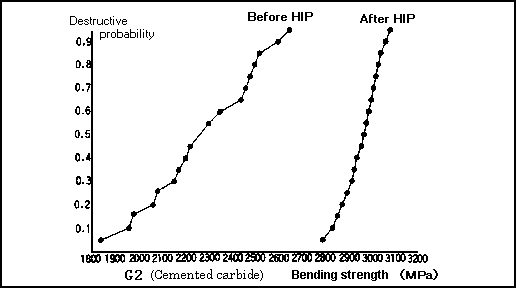
<Fig.4> Weibull plot of bending strength before and after HIP treatment
As shown above, the density and hardness of cemented carbide are not changed by HIP treatment. However, by the removal of fine pores, the bending strength is largely improved and the dispersion in strength becomes very small to increase reliability.
Ceramics
Ceramics are composed of strong crystals created by ionic bond and covalent binding. As a result, ceramics are very hard, strong against deformation and stable under high temperature because, in such a state, movement of atoms is small. To the contrary, this means that ceramics are difficult to sinter and it is difficult to obtain a compact sintered body of ceramic. If adding a large amount of sintering assistant to improve the sintering effect, it is possible to make a compact ceramic but its original characteristics are lost. Further, though it is possible to lower the porosity by increasing the sintering temperature, crystal particle becomes coarse and mechanical properties are deteriorated. HIP however is possible to produce compact ceramics without raising those problems. Table 2 shows the change in mechanical properties of ceramics by HIP.
<Table 1> Effect of HIP treatment on mechanical properties of cemented carbide (G2)
As shown in the table, ceramics become compact nearly up to the theoretical density by HIP treatment and the mechanical properties are improved largely. Moreover it is possible to obtain an extremely flat ground surface by eliminating the residual pores by HIP. Fig.5 shows an example of improving the surface roughness by HIP treatment.
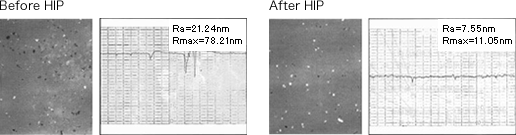
<Fig.5> Surface roughness of silicon nitride ceramics by HIP treatment
As explained above, HIP is a process that is very effective for compacting cemented carbide and ceramics, improving their mechanical properties and reliability.
NIPPON TUNGSTEN CO., LTD. started the study of forming and sintering fine ceramic powder by HIP in 1970s and, in 1977, succeeded in the development of high-dense alumina cutting tool by HIP for the first time in Japan. Since then, NIPPON TUNGSTEN CO., LTD. has been applying HIP technology to various products in order to make full use of the original characteristics of raw material.